News
Common faults and troubleshooting methods for material testing machines
Release time:2022-07-01 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
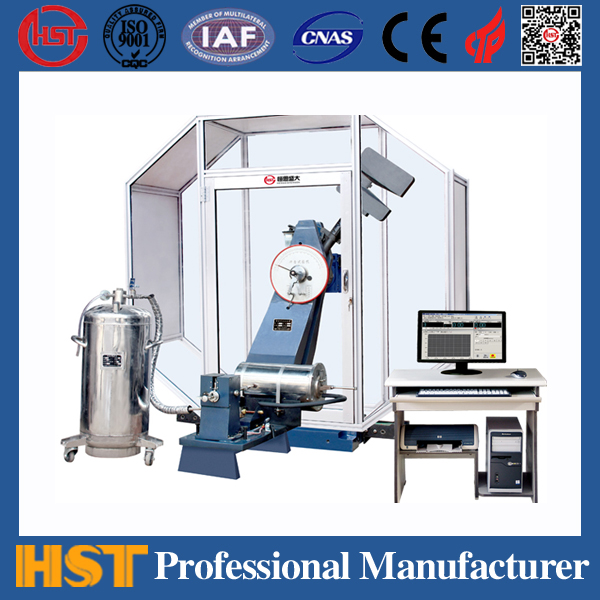
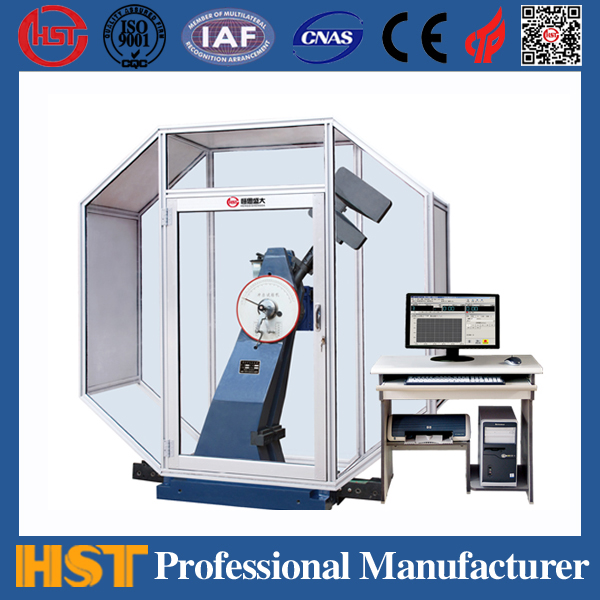
The metal products industry cannot do without material testing machines, and users of product companies cannot do without testing machines. However, quality objections caused by test machines failures are not uncommon. Material testing machines often fail. Here is an analysis of the causes of common failures:
Common faults: During the loading process of the test machine, the fuselage vibrates, the pointer rotates unsteadily, and the value cannot be read accurately:
The vibration source that may cause resonance around the test machine should be eliminated first, and then observe whether the machine installation foundation is solid and check whether the motor is faulty. After these faults are discharged, the pointer is still unstable, so consider whether there is air in the oil circuit system.
The method is: start the oil pump, close the oil return valve, so that the main piston rises for a certain height, and then open the oil return valve to allow the oil to flow back to the oil tank from the main oil cylinder of the oil pump through the oil return valve. This cycle can be performed for a period of time and the air in the main cylinder can be discharged. Then unscrew the screws in the exhaust hole of the fuel tank and tighten when the oil emitted does not contain bubbles.
In addition, the high-pressure oil pipe of the oil pump can also be removed and the motor can be started to completely remove the air in the oil pump. For testing machines that are used for a long time, oil should be changed regularly and the tooth rods, gears, pointers and screws of the force-testing part should be cleaned. (It should be noted here that when cleaning the reel, the diameter of the replaced string should meet the requirements, and the direction and number of turns on the reel should be appropriate.) The oil is too dirty and sometimes the pressure of the oil supply valve will be changed due to blockage of debris, causing the oil volume to circulate unevenly. The lengths of the two triangle belts connected to the oil pump are inconsistent, the plunger in the oil pump does not work normally or the gaps between the seven sets of oil distribution valves will cause vibration of the test machine.
Common faults: The dial pointer is poorly sensitive, and it stops in the middle after unloading, or the zero position often changes:
1. The pulleys and tracks on the tooth rods are too dusty and rusted. At this time, you need to remove and clean it, and add a little watch oil. The pointer rotation shaft is dirty and should be cleaned.
2. If there is contact between the tooth rod tablet and the tooth rod, it should be loosened.
3. If the buffer oil return condition is poor, it should be adjusted or cleaned. (Refers to the detours being blocked)
4. The belt on the force-testing piston is falling off or too loose (makes the piston unable to operate at a uniform speed). When the friction force of the force-testing piston increases or gets stuck in the oil cylinder, use chromium oxide grinding paste to grind until it is normal.
5. There are obstacles during the lifting process of the pendulum, or the pendulum shaft is too dirty or rusted, causing the pointer to return to zero and change greatly.
Common faults: During tensile tests, the sample fracture is always broken on both sides. If this situation occurs, the installation of the main body part of the test machine should be considered first, and this reason should be ruled out, and then the following three aspects should be ruled out.
1. When clamping the jaws are not placed properly, the jaws should be clamped symmetrically as required:
2. The jaws are of poor quality and damage to the teeth. In addition to affecting the jaws, the sample is slipped during the test, making it difficult to identify the yield point. The jaws should be replaced at this time.
3. The lifting guide wheel is not adjusted properly, so that the upper and lower jaws are not centered. A test rod should be processed, and after the upper and lower jaws are tightened, use a dial gauge to measure with two force columns until the adjustment is qualified.
Common faults: The pendulum position is abnormal, and the pendulum rod is not marked vertically.
The main reason is that the oil has too much viscosity or the oil is too dirty. Exclusion method: Replace oil with appropriate viscosity.
The force measuring piston rotates with great friction or does not rotate. Troubleshooting method: Check whether the test machine is level and troubleshoot the force-testing piston.
There is unstable friction. Exclusion method: Clean the swing shaft bearing, tooth rod, pointer, and lug, adjust the level of the test machine to reduce the existing unstable friction.
Common faults: The hammer returns to the position abnormally, sometimes fast and sometimes slow:
Normally, just rotate the buffer to the appropriate position. However, if the oil hole of the buffer is blocked, or the steel ball of the buffer valve has a stolen property with the inlet contact part or the gap is too large, the buffer will fail. The solution is to clean the buffer valve and adjust the gap between the steel ball and the valve seat to about 0.5mm. Place the oil needle knob to reduce the gap between the oil needle and the valve body, and relist the mark of the A.B.C weight. Also, when the temperature has a great influence, the oil can be replaced appropriately.
Common faults: The passive needle cannot stop well in any position and does not coincide with the main needle.
The removal method is to remove the dial glass, adjust the passive needle spring screw, and adjust the pointer to coincide with the main needle.
Common faults: When loading, the oil circuit system is severely leaking or the oil pipe is broken:
Check whether the joints of the oil circuit system are tightened. If you need to replace the gasket, replace it in time. If the oil pipe is broken, then the oil pipe with higher strength needs to be replaced. In addition, you must observe whether the oil supply valve and relief valve piston are pressed to death or are installed in reverse.
Recommended productsPRODUCTS