Company News
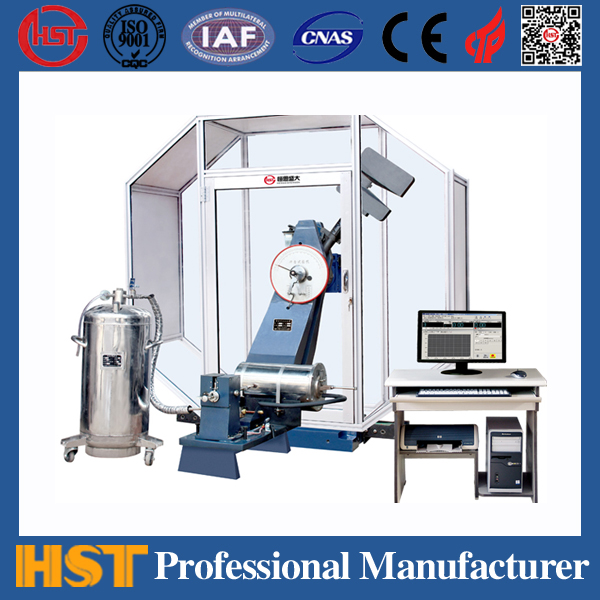
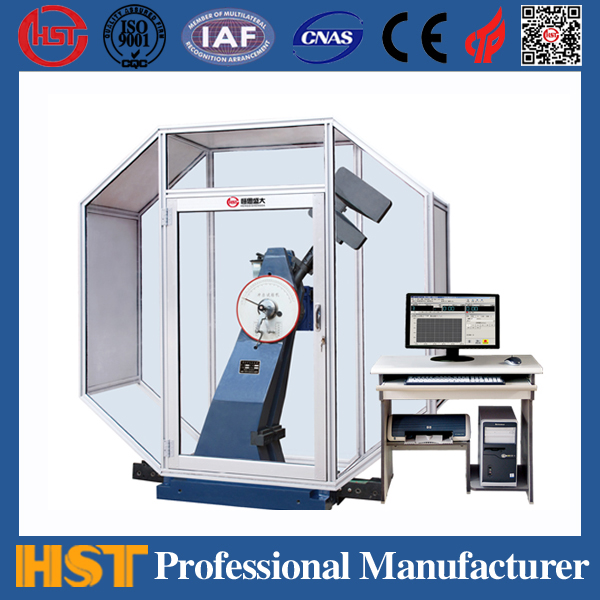
Classification of impact testing machines
Release time:2018-11-23 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
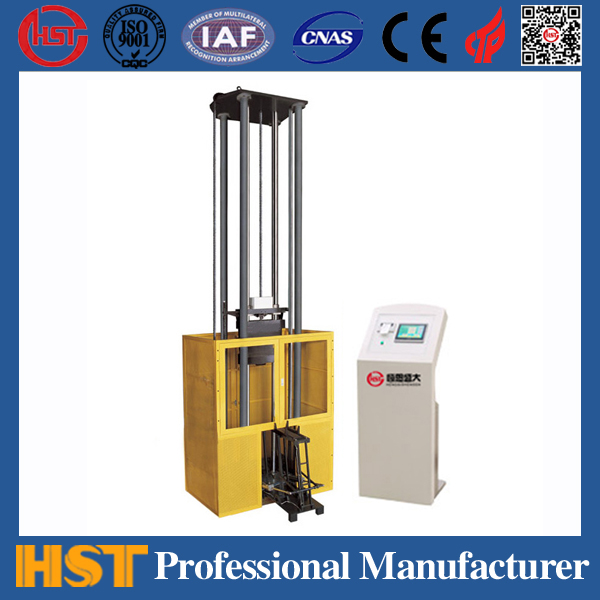
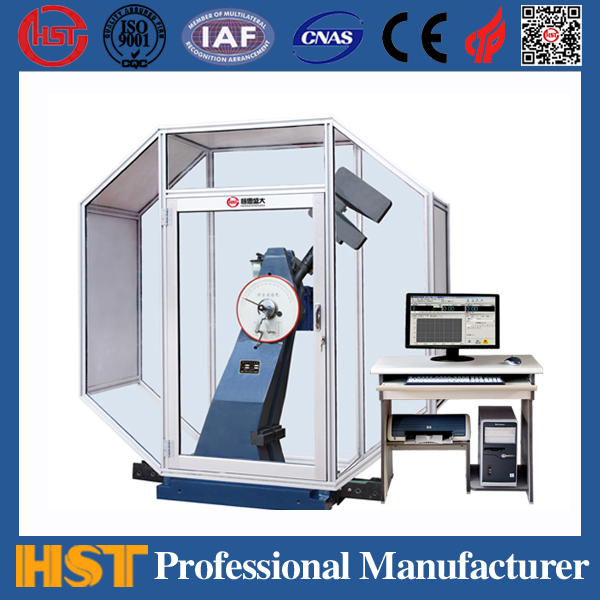
The choice of pendulum testing machine, the common impact test machine on the market is now pendulum type. Most test machines are equipped with different accessories (hammer head and sample fixture) to complete the Izod test, the Kabi test, and the tensile-impact test. There are many similarities between the Izod test and the Kabi test. The samples used in both tests can be obtained by molding or cut from a large "eight"-shaped tensile sample. The sample size for Izod's test is 2.5x0.5 in , while the sample size for Kabi's test is 5x0.5 in . The thickness of the two test samples depends on the specifications of the material being tested (in Izod tests, the commonly used thickness is 1/8 in). Before the test, the sample must be cut and the sample must be adjusted to the required temperature and humidity. Each group of tests should have 10 fewer samples, and the average value of the test results should be taken. The unit of Izod's test is lt-lb/in, and the unit of Kabi's test is joule/m2.
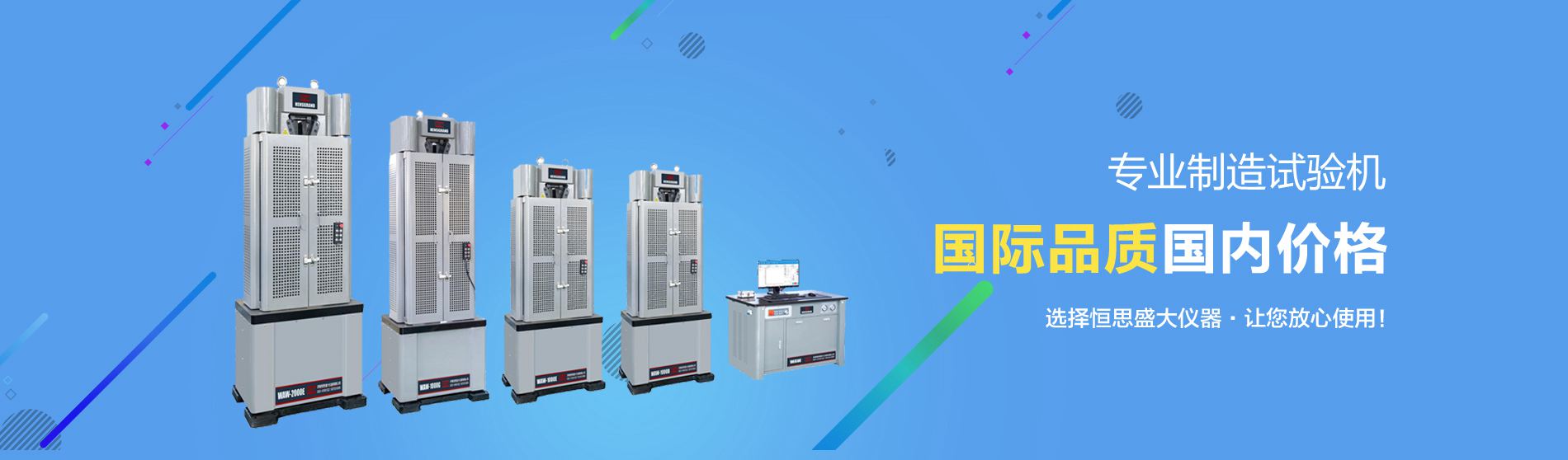
The hammer tester, including the traditional Gardner pointed hammer and mechanical drop tower, is used to measure the total energy that causes damage to the trim, sheet, film, tube, box and molded products. Simple and simple are Gardner hammer test (ASTM D5054) machines for rigid plastics and pointed hammer test (ASTM D1709) machines for films and elastic sheets. This device places an object of a certain weight on the end of the block or pointed hammer head. After lifting the hammer head to a certain height, it falls freely toward the fixed sample. For basic devices, the commonly used hammer head weights are 2, 4 and 8 pounds, and the hammer head weights used in mechanical drop towers are 50 pounds or more. There are many test procedures, and each group of tests must have as many as 30 typical samples. Energy calculation mainly involves ft-lb and in.-lb, or grams (g) and the radius of the impact head, that is: hammer head weight and impact height. The selection of impact height and hammer head shape has not been standardized. Instron's Lio believes: "The specific value can be determined based on the strain rate of the polymer. The energy of a 10-pound weight falling from a height of 2 feet is the same as the energy of a 2-pound weight falling from a height of 10 feet. However, due to the different impact speeds, they produce different effects." Large film manufacturers and their resin suppliers use pointed hammer test machines in large quantities.
Traditional test machines have the advantages of simple operation, low price, and long-term use history, so they have always been loved by the majority of users. Especially for pendulum testing machines with notched-Izod impact tests, this is a commonly selected test in the United States. But traditional methods of experimentation have begun to be challenged. Researchers from some raw material suppliers have already raised objections to these simple trials due to low precision and poor repeatability. New instruments improve some of these defects. And there was a phenomenon of abandoning the Izod impact report (one of the ASTM D256 test protocol) and turning to the use of the Kerby test (ISO 179). In Europe, another pendulum test method is mainly used. The main force driving this change comes from the automotive industry, which is part of its global standardization outcome.
At present, the mature data obtained through instrumentation and "real" impact tests are mainly used within raw material suppliers and compounding manufacturers. The raw material specification data required by processors and their customers are still mainly based on traditional Izod and Dart impact test data. In fact, some data suggest that more and more plastic processors are more willing to conduct shock tests on their own to ensure consistent performance of their products, rather than relying solely on data provided by raw material suppliers.
The design of traditional test devices has also been improved over the past decade. For example, in the pendulum test machine, the original dial has gradually shifted to a digital reader, and many test projects have been automated. But most of the systems used are still not improved. Many innovations combine mechanical hammer dropping and pendulum testing machines into one. However, except for a few test rooms that require hundreds of tests per day, there are very few fully automatic systems that can automatically load samples.
What is impact test? Harry Yohn, marketing manager at Tinius Olsen Test Equipment Co., Ltd., explained that impact testing is to load the sample at a high speed and then measure the changes in the test piece. The damage of the specimen is divided into two steps: First, the impact energy causes cracks to occur in the specimen, and then, the specimen bears a greater impact force to expand and damage the cracks. Among the two basic types of plastic impact testing machines, the pendulum impact testing machines are used in Izod and Charpy tests, and tensile impact measures the energy absorbed by the sample and caused its damage. Another type is the drop hammer test - Gardner drop hammer is suitable for steel materials, and pointed drop hammer is suitable for films. These are typical pass/fail type tests that give the average impact energy that destroys the specimen over 50% of the time.
Traditional tests are sufficient for quality control purposes, but they do not provide a mechanism of damage or cause of damage to the finished product. Moreover, traditional impact tests can only measure the energy required to rupture the specimen. Instrumented impact tests provide curves generated by high-speed stress/strain data, through which they can distinguish toughness and brittle damage, and the energy that causes the crack to start and the energy that transmits. The latter can give many graphs that express the subtle differences in the toughness of the specimen, Yohn explained. In addition to the limitations of traditional impact experiments, there are other factors that promote the development of impact testing to instrumented impact. One of the key issues is that more and more products involve the fields of ≤‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐�
- Previous article:Tension tester fault resolution
- Next article:Basic features of spring fatigue testing machine
Recommended productsPRODUCTS