Company News
Partial special nouns for testing machines
Release time:2018-11-23 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
Product section
◆ Testing machine
A test machine is an instrument, system or device that tests and detects the strength, stiffness, hardness, elasticity, plasticity, toughness, ductility and surface and internal defects of materials (metallic materials, non-metallic materials), components, components and structures. Most test machines are technology-intensive high-tech products that integrate machine photoelectric and hydraulics, and most of them are metrological instruments. Test machines are widely used in the field and laboratories of industrial and mining enterprises, metrology and schools. Their application fields involve machinery, metallurgy, construction, aviation, aerospace, military industry, transportation, transportation, quality inspection, metrology, education, medical care and other industries.
The test machine industry mainly produces and manufactures the following eight categories of products: 1. Metal material testing machines; 2. Non-metallic material testing machines; 3. Force and deformation testing instruments (force sensors, force meters, displacement sensors, extensometers, accelerometers, etc.); 4. Packaging parts and process performance testing machines (including packaging drop test machines, packaging impact test machines, friction and wear test machines, bending test machines, straightening machines, etc.); 5. Balance machine (including on-site balance instruments); 6. Vibrating tables (including impact tables and collision test machines); 7. Non-destructive testing instruments (magnetic powder flaw detectors, X-ray flaw detectors, gamma ray flaw detectors, ultrasonic flaw detectors, eddy current flaw detectors, acoustic emission detectors, etc.); 8. Functional accessories of the test machine and testing instruments and equipment related to the test machine.
◆ Basic knowledge of test machines
1. What is a test machine
The test machine we usually see should actually be called a material test machine, which is an instrument used to test the mechanical and physical properties of various materials or components.
2. Classification of material testing machines
There are many classification methods for material testing machines, and the common ones are:
1) According to the type of output source, there are mainly motor, hydraulic, pneumatic, electromagnetic, etc.;
2) According to the indicator type of measurement, the main ones are digital display and pointer;
3) The main relationship between the load and time of the sample is: static machine and fatigue machine.
4) According to the control method, the main types of control are open-loop control (manual control) and closed-loop control (automatic control). For closed-loop control, the types of control include: speed control, load control, deformation control, and position control.
5) According to the purpose, there are mainly general-purpose machines (universal machines) and special-purpose machines.
6) Testing methods and testing machines
Generally speaking, there are only two types of test machines: one is the force in a linear direction such as pulling or pressure. The pulling, pressing, bending, shearing, peeling, tearing, penetrating, wear, etc. we usually see, all belong to this category, and the other is the force in a circular direction, such as twisting.
III. Detection and control
Detection and control are two different concepts, but they are inseparable. Generally speaking, for a specific system, under a specific test condition, it only controls a specific parameter, such as the electric pull of our company, which only controls the movement speed of the test bench, and generally there are more than one detection amount. For example, electric pulling, there are loads, displacements, deformations and other detection links.
4. Open-loop control and closed-loop control
(1) Open-loop control:
Open-loop control cannot be used to control the input quantity by changing the output signal, and manual control is generally open-loop control. For example, manually converting the fan gears to achieve speed control. The difference between open-loop control and closed-loop control is: whether there is feedback. There is no open loop, there is no closed loop. The so-called feedback refers to the effects caused by behavioral actions. Simple example "You slapped someone else, you saw his blushing, this is the feedback you get from your eyes" closed loop system example:
A fully automatic washing machine. When adding water to the washing machine, an infrared sensor inside scans the water level to the height. When the water level is right, the washing machine will automatically stop adding water. If it is an open-loop-controlled washing machine, the water level must be seen by people. When people think the water level is right, they will turn off the faucet.
(2) Closed-loop control
Closed-loop control is a basic concept of cybernetics. Refers to a control relationship in which the controlled output is returned to the input terminal as the control in a certain way and exerts control influence on the input terminal. Generally, the withdrawal quantity and the input quantity are opposite to the phase, so it is called negative feedback control. Automatic control is usually closed-loop control. For example, the temperature control of household air conditioners
The output end feeds back to the input end and participates in re-control of the output end. This is the purpose of closed-loop control, and this purpose is achieved through feedback. Positive feedback and negative feedback are two common basic forms of closed-loop control.
V. Test speed
The speed of tensile or compressing the test piece during the test is mm/min.
6. Measurement accuracy
It refers to the accuracy of the measurement. Including force measurement accuracy, speed accuracy, deformation accuracy, and displacement accuracy.
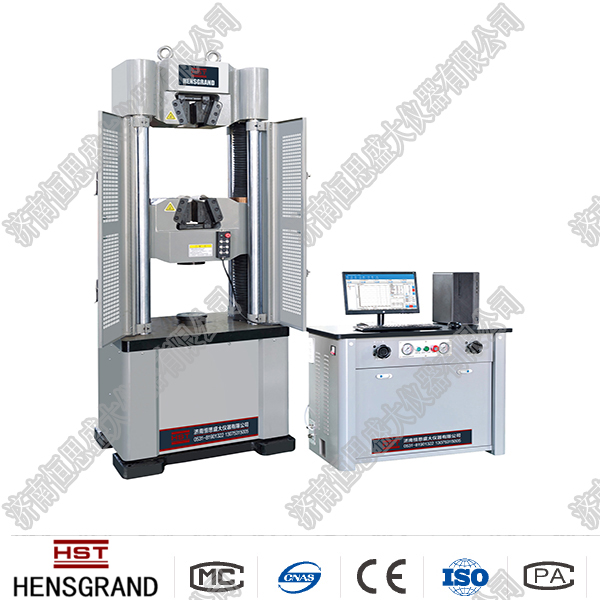
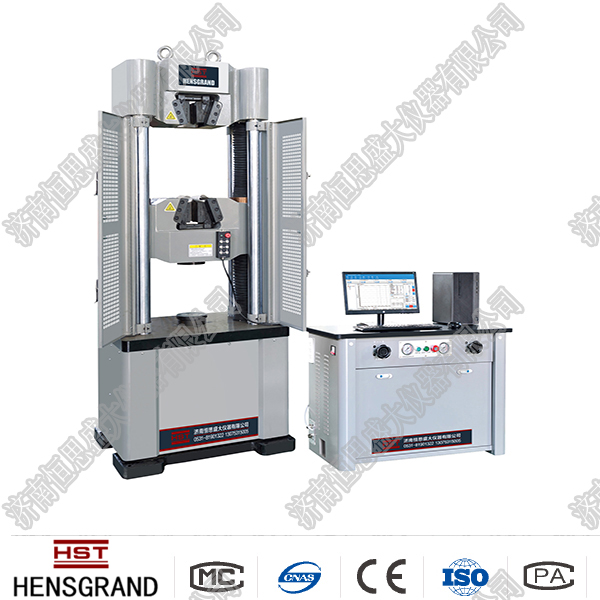
◆ Tension test machine
Tension machine is also called tensile testing machine. Tension machine is a mechanical after-force test machine used to test materials such as tensile, compression, bending, shearing, and peeling. It is suitable for various physical and mechanical properties testing of plastic sheets, pipes, special profiles, plastic films, rubber, wires, cables, waterproof rolls, metal wires and other materials. Its use industry scope covers: scientific research institutes, commodity inspection and arbitration institutions, colleges and universities, as well as rubber, tires, plastics, wires and cables, shoemaking, leather, textile, packaging, building materials, petrochemicals, aviation and other industries. It is indispensable for material development, physical properties test, teaching research, quality control, feed inspection, and random inspection of production lines.
◆ Mechanical main frame structure
(1) Single-arm structure: a frame structure supported by one or more groups of light rods and a set of lead screw transmission. It has the advantages of small size and low price. However, due to mechanical strength, when the test force is above 10KN, the mechanical structure will be deformed, which will affect the test results, so it is only used for models below 5KN.
(2) Door-type structure: a frame structure supported by two or more groups of light bars and two groups of lead screws. It has the advantages of large power, large test space and stable structure. Used for models above 10KN.
◆ Test itinerary (test space)
The range of movement of the cross beam in the test machine determines the volume, extension length, etc. of the test piece that can be tested.
◆ Output result.
The output results of the test results include: elongation, tensile strength, constant elongation, fixed elongation value, yield strength, elastic modulus, test force, etc. When operating with a computer, the output is relatively comprehensive.
◆ Transmission method
There are lead screw drives and rack drives. The former is expensive, used for high accuracy and has high repeatability for tests; the latter is cheap, used for low accuracy and has low repeatability for tests.
There are geared and chain drives, the former is expensive for high precision, and the latter is cheap for low precision.
◆ Testing machine
A test machine is an instrument, system or device that tests and detects the strength, stiffness, hardness, elasticity, plasticity, toughness, ductility and surface and internal defects of materials (metallic materials, non-metallic materials), components, components and structures. Most test machines are technology-intensive high-tech products that integrate machine photoelectric and hydraulics, and most of them are metrological instruments. Test machines are widely used in the field and laboratories of industrial and mining enterprises, metrology and schools. Their application fields involve machinery, metallurgy, construction, aviation, aerospace, military industry, transportation, transportation, quality inspection, metrology, education, medical care and other industries.
The test machine industry mainly produces and manufactures the following eight categories of products: 1. Metal material testing machines; 2. Non-metallic material testing machines; 3. Force and deformation testing instruments (force sensors, force meters, displacement sensors, extensometers, accelerometers, etc.); 4. Packaging parts and process performance testing machines (including packaging drop test machines, packaging impact test machines, friction and wear test machines, bending test machines, straightening machines, etc.); 5. Balance machine (including on-site balance instruments); 6. Vibrating tables (including impact tables and collision test machines); 7. Non-destructive testing instruments (magnetic powder flaw detectors, X-ray flaw detectors, gamma ray flaw detectors, ultrasonic flaw detectors, eddy current flaw detectors, acoustic emission detectors, etc.); 8. Functional accessories of the test machine and testing instruments and equipment related to the test machine.
◆ Basic knowledge of test machines
1. What is a test machine
The test machine we usually see should actually be called a material test machine, which is an instrument used to test the mechanical and physical properties of various materials or components.
2. Classification of material testing machines
There are many classification methods for material testing machines, and the common ones are:
1) According to the type of output source, there are mainly motor, hydraulic, pneumatic, electromagnetic, etc.;
2) According to the indicator type of measurement, the main ones are digital display and pointer;
3) The main relationship between the load and time of the sample is: static machine and fatigue machine.
4) According to the control method, the main types of control are open-loop control (manual control) and closed-loop control (automatic control). For closed-loop control, the types of control include: speed control, load control, deformation control, and position control.
5) According to the purpose, there are mainly general-purpose machines (universal machines) and special-purpose machines.
6) Testing methods and testing machines
Generally speaking, there are only two types of test machines: one is the force in a linear direction such as pulling or pressure. The pulling, pressing, bending, shearing, peeling, tearing, penetrating, wear, etc. we usually see, all belong to this category, and the other is the force in a circular direction, such as twisting.
III. Detection and control
Detection and control are two different concepts, but they are inseparable. Generally speaking, for a specific system, under a specific test condition, it only controls a specific parameter, such as the electric pull of our company, which only controls the movement speed of the test bench, and generally there are more than one detection amount. For example, electric pulling, there are loads, displacements, deformations and other detection links.
4. Open-loop control and closed-loop control
(1) Open-loop control:
Open-loop control cannot be used to control the input quantity by changing the output signal, and manual control is generally open-loop control. For example, manually converting the fan gears to achieve speed control. The difference between open-loop control and closed-loop control is: whether there is feedback. There is no open loop, there is no closed loop. The so-called feedback refers to the effects caused by behavioral actions. Simple example "You slapped someone else, you saw his blushing, this is the feedback you get from your eyes" closed loop system example:
A fully automatic washing machine. When adding water to the washing machine, an infrared sensor inside scans the water level to the height. When the water level is right, the washing machine will automatically stop adding water. If it is an open-loop-controlled washing machine, the water level must be seen by people. When people think the water level is right, they will turn off the faucet.
(2) Closed-loop control
Closed-loop control is a basic concept of cybernetics. Refers to a control relationship in which the controlled output is returned to the input terminal as the control in a certain way and exerts control influence on the input terminal. Generally, the withdrawal quantity and the input quantity are opposite to the phase, so it is called negative feedback control. Automatic control is usually closed-loop control. For example, the temperature control of household air conditioners
The output end feeds back to the input end and participates in re-control of the output end. This is the purpose of closed-loop control, and this purpose is achieved through feedback. Positive feedback and negative feedback are two common basic forms of closed-loop control.
V. Test speed
The speed of tensile or compressing the test piece during the test is mm/min.
6. Measurement accuracy
It refers to the accuracy of the measurement. Including force measurement accuracy, speed accuracy, deformation accuracy, and displacement accuracy.
◆ Tension test machine
Tension machine is also called tensile testing machine. Tension machine is a mechanical after-force test machine used to test materials such as tensile, compression, bending, shearing, and peeling. It is suitable for various physical and mechanical properties testing of plastic sheets, pipes, special profiles, plastic films, rubber, wires, cables, waterproof rolls, metal wires and other materials. Its use industry scope covers: scientific research institutes, commodity inspection and arbitration institutions, colleges and universities, as well as rubber, tires, plastics, wires and cables, shoemaking, leather, textile, packaging, building materials, petrochemicals, aviation and other industries. It is indispensable for material development, physical properties test, teaching research, quality control, feed inspection, and random inspection of production lines.
◆ Mechanical main frame structure
(1) Single-arm structure: a frame structure supported by one or more groups of light rods and a set of lead screw transmission. It has the advantages of small size and low price. However, due to mechanical strength, when the test force is above 10KN, the mechanical structure will be deformed, which will affect the test results, so it is only used for models below 5KN.
(2) Door-type structure: a frame structure supported by two or more groups of light bars and two groups of lead screws. It has the advantages of large power, large test space and stable structure. Used for models above 10KN.
◆ Test itinerary (test space)
The range of movement of the cross beam in the test machine determines the volume, extension length, etc. of the test piece that can be tested.
◆ Output result.
The output results of the test results include: elongation, tensile strength, constant elongation, fixed elongation value, yield strength, elastic modulus, test force, etc. When operating with a computer, the output is relatively comprehensive.
◆ Transmission method
There are lead screw drives and rack drives. The former is expensive, used for high accuracy and has high repeatability for tests; the latter is cheap, used for low accuracy and has low repeatability for tests.
There are geared and chain drives, the former is expensive for high precision, and the latter is cheap for low precision.
- Previous article:8 equipment and uses of thermal insulation material universal testing machine
- Next article:Classification and use of hardness meter
Recommended productsPRODUCTS