Company News
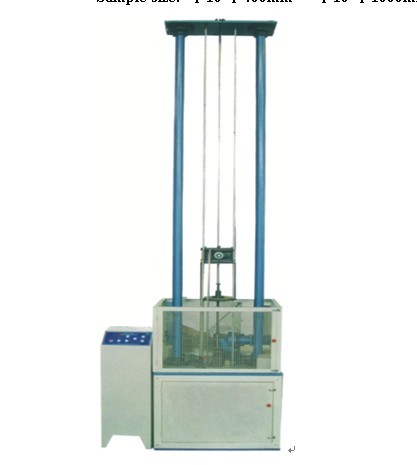
Test data of universal testing machine
Release time:2018-11-23 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
The universal testing machine will reflect the physical characteristics of various materials while detecting materials. At the same time, various data will also be reflected on the display screen of the test machine to analyze the indicators below. One of the methods is mainly used to check whether the material meets the specified standards and to study the properties of the material.
Plasticity refers to the ability of metal materials to produce plastic deformation without damage under load. Common plasticity indicators are elongation and cross-section.
Shrinkage rate. Elongation, also known as elongation, refers to the percentage of the ratio of the total elongation to the original length after the material sample is broken under tensile load, and is tabled using δ.
Show. The cross-section shrinkage refers to the percentage of the ratio of the area of the cross-section to the original cross-sectional area after the material sample is broken under tensile load.
express.
Performance indicators Tensile tests can determine a series of strength indicators and plastic indicators of materials. Strength usually refers to the external force of the material
The ability to resist elastic deformation, plastic deformation and fracture. When the material is subjected to tensile loads, it continues to occur when the load does not increase.
The phenomenon of plastic deformation is called surrender. The stress during yield is called the yield point or physical yield strength, which is represented by σS (Pa). project
There are many materials on which there is no obvious yield point, and the stress value when the residual plastic deformation of the material is 0.2% is usually used as the yield strength.
It is called the conditional yield limit or conditional yield strength, expressed as σ0.2. The stress value reached by the material before breaking is called tensile strength or strength
The degree limit is expressed by σb (Pa).
Conditional yield limit σ0.2, strength limit σb, elongation δ and cross-section shrinkage ψ are the four properties that are often measured in tensile tests.
Standard. In addition, the elastic modulus E, proportional limit σp, elastic limit σe, etc. of the material can also be measured.
During the test, the tester stretches the sample evenly at a specified rate, and the tester can automatically draw a tensile curve chart. For low carbon steel and other plastics
When the sample is stretched to the yield point, the force measuring pointer will jitter significantly, and the upper and lower yield points (and) can be divided into
When calculating, it is often taken. The δ and ψ of the material can be combined with the specimens after the test fracture, measured their elongation and reduced cross-section and calculated.
Test method Tensile test is carried out on a material testing machine. Test machines include mechanical, hydraulic, electro-hydraulic or electronic servo type.
Mode. The specimen type can be of full cross-section of the material or can be processed into round or rectangular standard specimens. Some physical samples such as steel bars and wires
Generally, there is no need to process but maintain its full cross-section for testing. When preparing the sample, the material structure should be avoided from being affected by cold and hot processing, and ensure that
A fixed finish.
Tensile curve diagram The tensile curve drawn by the test machine is actually a load-elongation curve, such as load coordinate value
Dividing the elongation coordinate value by the original cross-sectional area of the sample and the gauge distance of the sample respectively, a stress-strain curve can be obtained. In the picture
The op part is straight, and at this time the stress and strain become proportional, and its ratio is the elastic modulus, and Pp is the load when it is proportional.
The stress of the load and p point is the proportional limit σp. When continuing to load, the curve deviates from op until point e, when the load is unloaded,
The sample can still be restored to its original state, and if the sample passes through e, it cannot be restored to its original state. The stress at point e is the elastic limit σ
e. In engineering, it is difficult to measure the true σe, and the stress when the residual elongation of the sample reaches 0.01% of the original gauge distance is the elastic limit, with σ
0.01 means. Continue to load, the sample deforms along the es curve to reach the s point, and the stress at this point is the condition of the yield point σS or the residual elongation is 0.2%.
Yield strength σ0.2. Continue to increase the load through point s to point b before the pull-off. At this time, the load divided by the original cross-sectional area is the strength limit.
σb. After point b, the sample continues to elongate, while the cross-sectional area decreases, and the load-bearing capacity begins to decline until point k breaks. Load at the moment of breakage
The ratio to the cross section at the fracture is called the fracture strength.
- Previous article:Viewing test data of ten thousand test machines
- Next article:Precautions for use of tensile testing machine
Recommended productsPRODUCTS