News
Important factors affecting the performance, accuracy and life of tensile testing machines
Release time:2022-06-24 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
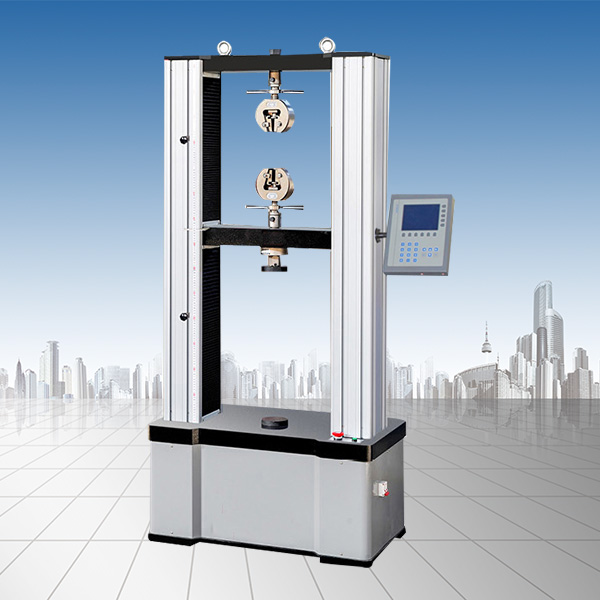
The tensile tester is a high-precision and high-tech material testing equipment that can be used to test mechanical properties such as tensile, compression, bending, shear, and peeling on metal and non-metallic materials. The reason why it has become the main equipment for material testing is that it has the advantages of easy operation and high accuracy.
However, if we buy a tensile tester with unqualified quality due to price reasons, it may lead to inaccurate test data. If the experiment fails due to inexperienced human operation, it will greatly reduce its usefulness. The following is the high-power sharing of five important factors that affect the performance, accuracy and life of the tensile tester:
Factor 1: Tension tester value sensor, because the quality of the sensor determines the accuracy and force stability of the tester. At present, some electronic tension machines on the market use S-type sensors for small force values, and wheel-type sensors for large force values. The inside of the sensor is generally a resistive strain gauge type. If the accuracy of the strain gauge is not high or the anti-aging ability of the glue used to fix the strain gauge is not good or the material of the sensor is not good, it will affect the accuracy and service life of the sensor.
Factor 2: The ball screw drives the sensor movement component, because if there is a gap in the screw, the test data will be directly affected by the maximum deformation and elongation after break of the test. At present, some tensile testing machines on the market use ordinary T-shaped screws. In this case, the gap is relatively large, and the friction is relatively large, the service life is short.
Factor 3: The transmission system of the tensile tester. Currently, some electronic tensile machines on the market use reducers, and some use ordinary leather to drive. The main disadvantages of these two transmission methods: the first type requires regular lubricating oil, while the latter type cannot ensure the synchronization of the transmission affects the test results.
Factor 4: The power source (motor) of the tensile tester is also called a motor. At present, some electronic tensile machines on the market use ordinary three-phase motors or variable frequency motors. This motor uses analog signal control, slow control reaction, inaccurate positioning, generally, narrow speed, low speed, low speed, low speed, low speed, and low speed, and inaccurate speed control.
Factor 5: The measurement and control system of electronic tension machines (that is, software and hardware). At present, some electronic tension machines on the market use 8-bit microcontroller control, with low sampling rate and poor anti-interference ability. In addition, if the number of bits of the AD converter is low, the measurement will not be accurate.
Recommended productsPRODUCTS