Company News
Analysis of the basic principles of test data of universal testing machine
Release time:2018-11-23 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
Analysis of the basic principles of test data of universal testing machine:
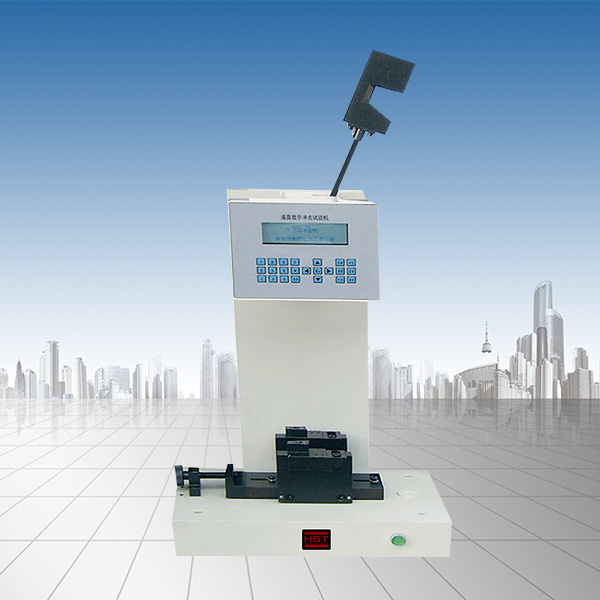
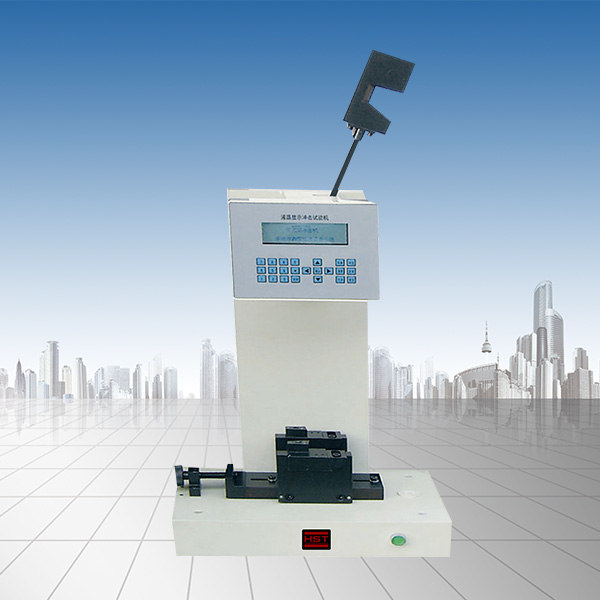
The universal testing machine is not just a tensile test, but can be used to replace different auxiliary tools. But how do you measure the test data of the universal testing machine? The following Hengsisheng editor will explain it in detail.
1. Measurement of force value
Generally speaking, the output flag code of the sensor is often weak in length, and only a few mV is needed in the world. Assuming that the flag code is directly measured, the length is often hard, and it cannot be satisfied with high-precision measurement. Therefore, it is necessary to expand this weak flag code through the expander. The expanded flag code voltage can reach 10V. At this moment, the flag code is imitated as the flag code. This imitated as the flag code is changed to a digital flag code through a multi-channel switch and A/D conversion chip, and then data processing is carried out. At this point, the measurement of the power of the universal test machine has come to an end.
2. Measuring deformation
By measuring by deformation measuring device, it is used to measure the deformation of the sample during the test process.
There are two chucks on the device, which are connected to the photoelectric encoder installed on the top of the measuring device via a series of transmission structures. When the distance between the two chucks changes, the axis of the femorable photoelectric encoder changes, and the photoelectric encoder will have a pulse flag output. Then the disposer disposes the flag code to obtain the deformation of the sample.
After measuring the force sensor, expander and data processing system, the commonly used force sensor is a strain gauge sensor.
The so-called strain gauge sensor is a device that can turn a certain mechanical material into a power output device that is composed of strain gauge, elastic components and certain accessories (compensation components, protective covers, wiring sockets, and loaders). There are many types of strain gauge-type pull-and-pressure sensors, including cylindrical force sensors, spoke-type force sensors, S double-connected hole sensors, cross beam sensors, etc.
From the mechanics of materials, under the premise of small deformation, the strain at a certain point of an elastic element is proportional to the force exerted by the elastic element, and is also proportional to the change of elasticity. Taking the S-type sensor as an example, when the sensor is subjected to the tension force P, since a strain gauge is posted on the surface of the elastic element, the strain gauge is directly proportional to the magnitude of the external force P, so the strain gauge is connected to the measuring circuit, and its output voltage can be measured and then the magnitude of the force is measured.
The universal testing machine is not just a tensile test, but can be used to replace different auxiliary tools. But how do you measure the test data of the universal testing machine? The following Hengsisheng editor will explain it in detail.
1. Measurement of force value
Generally speaking, the output flag code of the sensor is often weak in length, and only a few mV is needed in the world. Assuming that the flag code is directly measured, the length is often hard, and it cannot be satisfied with high-precision measurement. Therefore, it is necessary to expand this weak flag code through the expander. The expanded flag code voltage can reach 10V. At this moment, the flag code is imitated as the flag code. This imitated as the flag code is changed to a digital flag code through a multi-channel switch and A/D conversion chip, and then data processing is carried out. At this point, the measurement of the power of the universal test machine has come to an end.
2. Measuring deformation
By measuring by deformation measuring device, it is used to measure the deformation of the sample during the test process.
There are two chucks on the device, which are connected to the photoelectric encoder installed on the top of the measuring device via a series of transmission structures. When the distance between the two chucks changes, the axis of the femorable photoelectric encoder changes, and the photoelectric encoder will have a pulse flag output. Then the disposer disposes the flag code to obtain the deformation of the sample.
After measuring the force sensor, expander and data processing system, the commonly used force sensor is a strain gauge sensor.
The so-called strain gauge sensor is a device that can turn a certain mechanical material into a power output device that is composed of strain gauge, elastic components and certain accessories (compensation components, protective covers, wiring sockets, and loaders). There are many types of strain gauge-type pull-and-pressure sensors, including cylindrical force sensors, spoke-type force sensors, S double-connected hole sensors, cross beam sensors, etc.
From the mechanics of materials, under the premise of small deformation, the strain at a certain point of an elastic element is proportional to the force exerted by the elastic element, and is also proportional to the change of elasticity. Taking the S-type sensor as an example, when the sensor is subjected to the tension force P, since a strain gauge is posted on the surface of the elastic element, the strain gauge is directly proportional to the magnitude of the external force P, so the strain gauge is connected to the measuring circuit, and its output voltage can be measured and then the magnitude of the force is measured.
Recommended productsPRODUCTS