Company News
The yield point, tensile strength, material yield strength, carbon steel knowledge of metal steel
Release time:2023-09-01 source:Jinan Hengsi Shanda Instrument Co., Ltd. Browse:
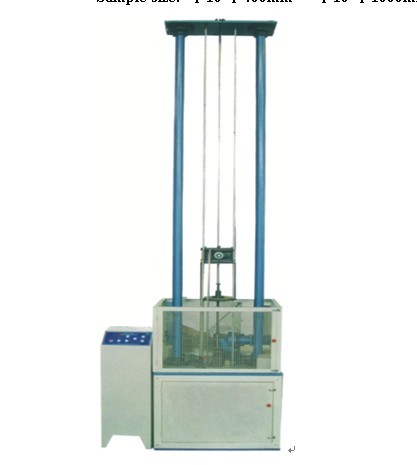
Carbon steel is the earliest and most used basic material in modern industry. Industrial countries around the world are working hard to increase the production of low alloy high strength steel and alloy steel, also pay great attention to improving the quality of carbon steel and expanding the variety and scope of use. At present, the proportion of carbon steel output in the total steel output of various countries remains at about 80%. It is not only widely used in construction, bridges, railways, vehicles, ships and various mechanical manufacturing industries, but also has been widely used in modern petrochemical industry, marine development and other aspects. The parts processed by carbon steel generally need to be subject to tensile strength detection and mechanical properties analysis, and may use material mechanical testing machines (electronic tensile testing machines, hydraulic universal testing machines) and friction and wear testing machines.
Introduction to basic knowledge of carbon steel
The carbon content is less than1.35%, except for iron, carbon and silicon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur and other heterocarbon steels within the limit, steel without other alloy elements. The performance of carbon steel mainly depends on the carbon content. The carbon content increases, the strength of the steel (data obtained through tensile tests and tensile tests), hardness increases, and plasticity, toughness, tensile strength and weldability decrease. Compared with other steels, carbon steel is the earliest to use, has a low cost, a wide range of performance and the largest amount of use.Suitable for nominal pressurePN≤32.0MPa, temperature of -30-425℃, water, steam, air, hydrogen, ammonia, nitrogen and petroleum products. Commonly used brands include WC1, WCB, ZG25, high-quality steel 20, 25, 30 and low alloy structural steel 16Mn.
Classification
1. Classify by chemical composition
Carbon steel can be divided into low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel according to chemical composition (i.e., carbon content).(1) Low carbon steel, also known as mild steel, has a carbon content ranging from 0.10% to 0.30% low carbon steel is easy to accept various processing such as forging, welding and cutting. It is commonly used in the manufacture of chains, rivets, bolts, shafts, etc. (2) Medium carbon steel Carbon steel with carbon content of 0.25% to 0.60%. There are a variety of products such as calm steel, semi-calm steel, boiling steel, etc. In addition to carbon, a small amount of manganese may also be contained (0.70% to 1.20%). According to product quality, it is divided into ordinary carbon structural steel and high-quality carbon structural steel. Good thermal processing and cutting performance, poor welding performance. The strength and hardness are higher than that of low carbon steel, while the plasticity and toughness are lower than that of low carbon steel. It can be used directly without heat treatment, and hot rolled materials or cold drawn materials, or after heat treatment. Medium-carbon steel after quenching and tempering has good comprehensive mechanical properties. The maximum hardness that can be achieved is about HRC55 (HB538), and σb is 600~1100MPa. Therefore, among various uses at medium strength levels, medium carbon steel is the most widely used. In addition to being a building material, it is also widely used in the manufacturing of various mechanical parts. (3) High-carbon steel is often called tool steel, with a carbon content ranging from 0.60% to 1.70%, which can be hardened and tempered. Hammers, crowbars, etc. are made of steel with a carbon content of 0.75%; cutting tools such as drills, wire taps, reamers, etc. are made of steel with a carbon content of 0.90% to 1.00%.
2. Classify by steel quality
According to the quality of steel, it can be divided into ordinary carbon steel and high-quality carbon steel. (1) Ordinary carbon structural steel, also known as ordinary carbon steel, has a wide limit on carbon content, performance range, and the content of phosphorus, sulfur and other residual elements. In China and some countries, it is divided into three categories according to the guarantee conditions for delivery: Class A steel (Class A steel) is a steel that guarantees mechanical properties. Class B steel (Class B steel) is a steel that ensures chemical composition. Special steel (Class C steel) is a steel that guarantees both mechanical properties and chemical composition, and is often used to make more important structural parts. Currently, the most commonly produced and used in China is A3 steel (Class A No. 3 steel) with a carbon content of about 0.20%, which is mainly used in engineering structures. Some carbon structural steels also add trace amounts of aluminum or niobium (or other carbide-forming elements) to form nitride or carbide particles to limit the growth of grains, strengthen the steel, and save steel. In China and some countries, in order to adapt to the special requirements of professional steel, the chemical composition and performance of ordinary carbon structural steel have been adjusted, thus developing a series of professional steels for ordinary carbon structural steels (such as bridges, buildings, steel bars, pressure vessel steel, etc.). (2) High-quality carbon structural steel Compared with ordinary carbon structural steel, the content of sulfur, phosphorus and other non-metallic inclusions is lower. According to the carbon content and use, this type of steel is roughly divided into three categories: ① Low carbon steel is less than 0.25% C, among which 08F, 08Al, which contains less than 0.10%, is widely used as deep-drawing parts such as automobiles, cans, etc. due to its good deep-drawing properties and weldability. 20G is the main material for manufacturing ordinary boilers. In addition, low carbon steel is also widely used as carburized steel and is used in the machinery manufacturing industry. ②0.25~0.60%C is medium-carbon steel, which is mostly used in tempering and tempering state to make parts of the machinery manufacturing industry. ③A high-carbon steel is greater than 0.6% C, which is mostly used to make springs, gears, rolls, etc. According to the different manganese content, it can be divided into two steel groups: ordinary manganese content (0.25-0.8%) and higher manganese content (0.7-1.0% and 0.9-1.2%). Tension testing machines, material testing machines, electronic tension testing machines and friction wear testing machines can be used to detect the mechanical properties and friction wear properties of carbon steel materials. Manganese can improve the hardenability of steel, strengthen ferrite, and improve the yield strength, tensile strength and wear resistance of steel. Usually, the mark "Mn" is added after the grade of steel with high manganese content, such as 15Mn and 20Mn, to distinguish it from carbon steel with normal manganese content.
3. Classified by purpose
According to its purpose, it can be divided into carbon structural steel and carbon tool steel. Carbon tool steelThe carbon content isBetween 0.65 and 1.35%, high hardness and wear resistance can be obtained after heat treatment, and are mainly used to manufacture various tools, cutting tools, molds and measuring tools (see tool steel). Carbon structural steel is divided into 5 grades according to the yield strength of steel: Q195, Q215, Q235, Q255, and Q275. Each grade is divided into A, B, C, and D grades due to different quality. There are four types at most, and some are only one; there are also differences in deoxygenation methods for steel smelting. Deoxidation method symbol: F——Boiling steel b——Semi-callised steel Z——Sallised steel TZ—Special calming steel Material detection and testing machines, electronic tension testing machines and friction wear testing machines can be used to detect the mechanical properties and friction wear properties of carbon steel materials.
Recommended productsPRODUCTS